testing for a rotator cuff tear|diagnosing a rotator cuff tear : importing Doctors can diagnose a torn rotator cuff by doing a physical examination, ultrasound, x-ray or MRI. These exams will help them . Play Fugitive Gold Slot. Fugitive Gold is an upcoming video slot by the renowned iGaming developer High 5 Games. The title features a popular Western theme and offers .
{plog:ftitle_list}
• Happy Family: Conditions Apply at IMDb• Happy Family: Conditions Apply on Amazon Prime Video Ver mais
They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms. Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X . Doctors can diagnose a torn rotator cuff by doing a physical examination, ultrasound, x-ray or MRI. These exams will help them .
Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but .When rotator cuff pathology is suspected, we can use some maneuvers to test the integrity of the four tendons that make up the cuff:- Infraspinatus- Supraspinatus- Subscapularis- Teres minorThe drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as: Doctors use a variety of tests to diagnose rotator cuff problems. Imaging tests, such as an MRI, are especially important for figuring out the specific cause of your pain. Differential Diagnoses . . Small rotator cuff .
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers the arm to .
A rotator cuff tear is a tear in the group of four tendons and muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. Learn about symptoms and how it is treated surgically or conservatively. . They may also have you complete additional tests to rule out other causes of shoulder pain. For example, if your pain extends down your shoulder and beyond your elbow .Occasionally, patients younger than 35 get partial tears of the rotator cuff. These tears may be associated with an injury. Partial rotator cuff tears are common in people who are overhead athletes (they play sports with an upper arm and shoulder arc over the head), such as pitchers in baseball. Partial rotator cuff tears in competitive .
Finally, the “painful arc sign” has high sensitivity (97.5 percent) as a single finding, making it helpful in ruling out rotator cuff tears when absent. 2 The test is performed by having the .
Imaging Tests. Other tests which may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include: . In some cases, tears in the rotator cuff tendons will be seen. An ultrasound may also be used to evaluate the rotator cuff tendon if you are unable to get an MRI. Related Media. Recovery . Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Rehabilitation Exercises . handout.
Learn about the 3 ways to test for a rotator cuff tear from Dr. Arlan Alburo of Orthopedic & Balance Therapy Specialists.If you are located in Northwest Indi.To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. Evidence [ edit | edit source ] Based on the Park et al [1] study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator .
Rotator cuff injury runs the full spectrum from injury to tendinopathy to partial tears, and finally complete tears. Age plays a significant role. . When considering a rotator cuff tear, there are variations in the tests noted above. If the patient cannot hold the empty can test position, it is called a drop arm test. Next is the external . The rotator cuff can also be injured in a single incident during falls or accidents. Risk factors. The following factors may increase the risk of having a rotator cuff injury: Age. The risk of a rotator cuff injury increases with age. Rotator cuff tears are most common in people older than 60. Some occupations.
Rotator cuff tear test. There are many special tests doctors use to diagnose rotator cuff tear. Although they are not always reliable, you likely have a rotator cuff tear if you feel pain when .This type of shoulder test, or rotator cuff injury test, is used to identify tears within the muscle group of the rotator cuff. Shoulder Shrug Test; This torn rotator cuff test checks if the patient imitates a shrug movement when trying to actively raise their arm. The patient is unable to raise the arm to a 90 degree elevation without raising .
Your rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that connects your shoulder blade to your upper arm bone (humerus).You use your rotator cuff to raise your arm overhead and to rotate your arm toward and away from your body. The rotator cuff sits in a small space between your humerus and the acromion (the upper part of your shoulder blade).An injury to the rotator cuff, such as a tear, may happen suddenly when falling on an outstretched hand or develop over time because of repetitive activities. . This test uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body. A rotator cuff may tear partly or . The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome.
Drop Arm Test. This simple test assesses the possibility of a rotator cuff tear. During the test, the patient (either sitting or standing) holds their arm straight out at a 90 degree angle, then slowly lowers the arm down to their side. The provider is looking for the patient’s ability to raise and lower the arm in a controlled manner.
Strength testing (manual muscles testing or with a hand held dynamometer) Clinical Tests: The diagnosis of an RC tendinopathy can be done in a clinic with the use of Cluster Tests: . For irreparable rotator cuff tears, alternative treatments include: Superior capsule reconstruction; Reverse total-shoulder arthroplasty; Acromioplasty; This is the most common way to diagnose a rotator cuff tear and what type of tear it is. MRI results can provide information about the tear that can help the provider make certain decisions .
Rotator cuff tear is one of the most common shoulder diseases. It is interesting that some rotator cuff tears are symptomatic, whereas others are asymptomatic. Pain is the most common symptom of patients with a tear. . The lift-off test to detect a subscapularis tear was introduced by Gerber and Krushell . If it is a rotator cuff tear, remember the #1 biggest mistake that prevents the proper healing of a rotator cuff tear: ignoring it. If you know you have a torn rotator cuff or even suspect it, seek treatment now rather than later, to prevent a small problem from developing into .
This can cause a full-thickness rotator cuff tear and can present with worsening pain and weakness, which can result in decreased function at the shoulder and impair activities of daily living. A case-control study looking at independent variables that may increase the likelihood of progression of partial-thickness rotator cuff tears to full . most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus. Infraspinatus Strength. technique. with the pateint's elbow in 90 degrees flexion, the arm at the side and internally rotated 45 degrees, external rotation strength can be checked against resistance by the examiner. Rotator cuff tears are painful but most don't require surgery. Learn the symptoms of a torn rotator cuff, the road to recovery, and when surgery may be needed. . If tests suggest a rotator cuff injury, imaging may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis. Rotator cuff injury test types. Which tests are performed may depend, in part, on whether .
When a rotator cuff tear is minor, taking a break from activities; applying ice regularly; and taking a nonprescription anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium, may be all you need to relieve the discomfort. In many cases, physical therapy also may help. A physical therapist can teach you exercises targeted to the . ROTATOR CUFF INJURY TESTS. The diagnosis of rotator cuff tendinitis or tear is usually based upon a careful medical history, the person's symptoms, and a physical examination. Again, as inflammation is seldom involved in these injuries, particularly if more than 36 hours have passed since the inciting event, most experts prefer the terms . As a rotator cuff tear becomes larger, retracted, and more degenerative in nature, the patient’s shoulder dysfunction will become more apparent as it becomes difficult for the rotator cuff as a group to function well. Shoulder Shrug Sign. The first special test I perform to diagnose a rotator cuff tear is the shoulder shrug sign.
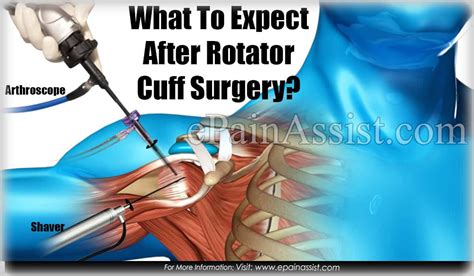
what to expect after rotator cuff surgery
shoulder test for rotator cuff
Ahrefs
testing for a rotator cuff tear|diagnosing a rotator cuff tear